Unit 6: Chemical Bonds
Reading
BJU Chemistry book: Ch. 6 "Chemical Bonds"
AP Classroom: Unit 2 "Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties" (continued)
AP Princeton Review: Unit 2 (continued)
Topics
Lab
Bombardier Beetle research assignment
Instructions below
BJU Chemistry book: Ch. 6 "Chemical Bonds"
AP Classroom: Unit 2 "Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties" (continued)
AP Princeton Review: Unit 2 (continued)
Topics
- Types of chemical bonds
- Lewis structures
Lab
- Nitrogen Compounds lab
- Density weblab
Bombardier Beetle research assignment
Instructions below
| Handout: chemical_bonding_chart - compares strengths of common bonds.pdf |
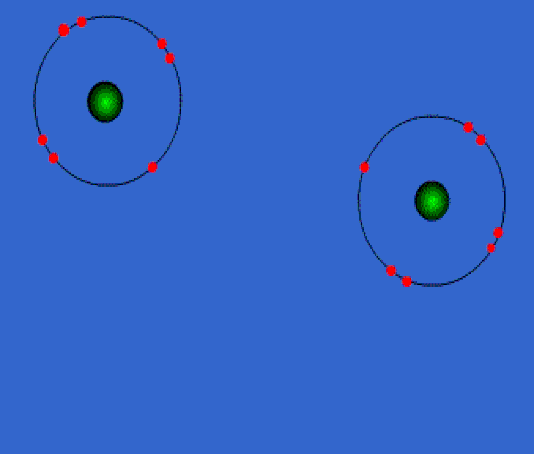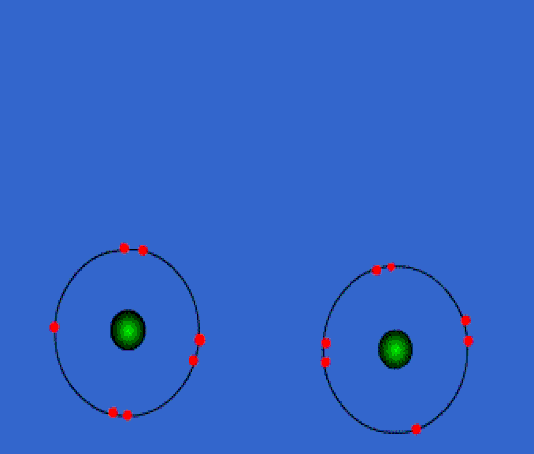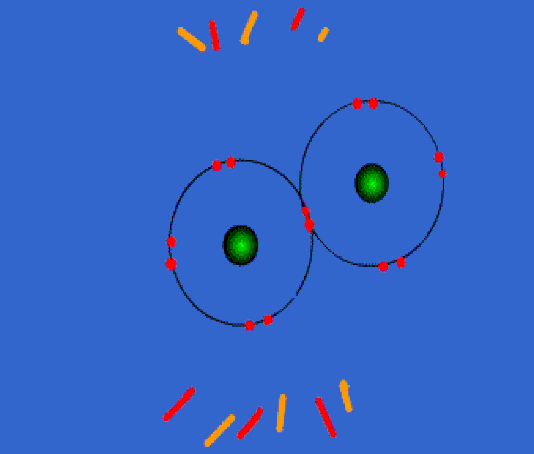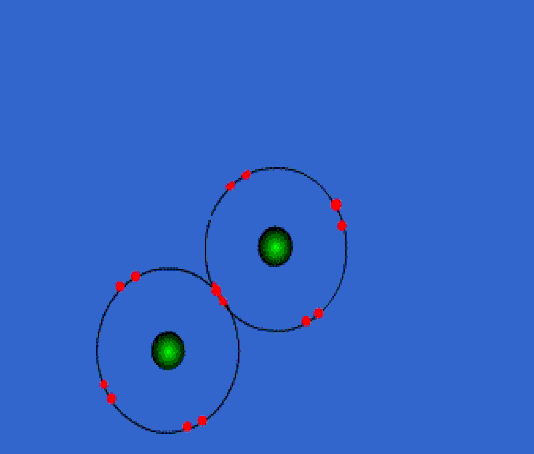
Below: Covalent bonding of two chlorine atoms. Once bonded, they both share 8 valence electrons. This is called an "octet". This forms a strong bond which is not easily broken. The two atoms have become a molecule of chlorine.
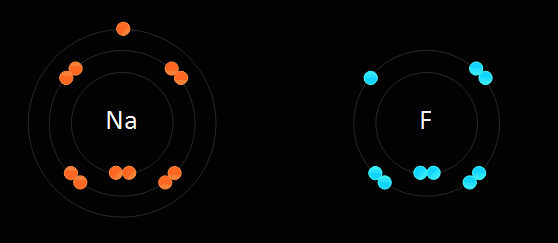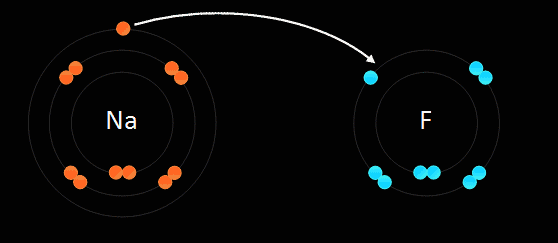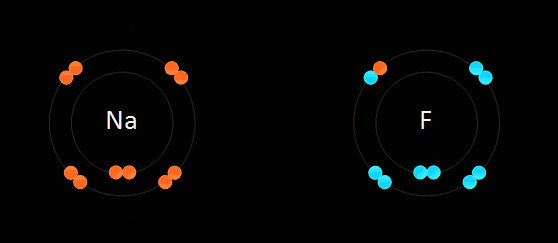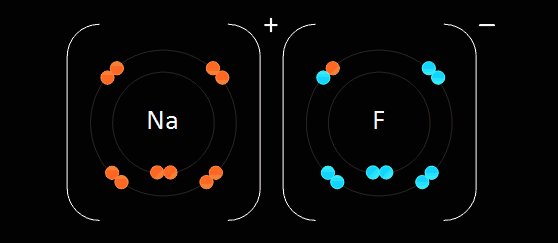
Below: Ionic bonding of a sodium atom (Na) and a fluorine (F) atom. The sodium entirely gives up its outer valence electron so that both atoms now have 8 valence electrons. As a result of this electron transfer, sodium now becomes a "cation" with a +1 charge, and fluorine becomes an "anion" with a -1 charge. Since positive and negative charges attract one another, the two ions bond together in an 'ionic bond'. If this is carried out in water (aqueous solution) they stay apart from one another. If the water is evaporated, they form a crystal in the bottom of the beaker. We discuss "solutions" later in the course...
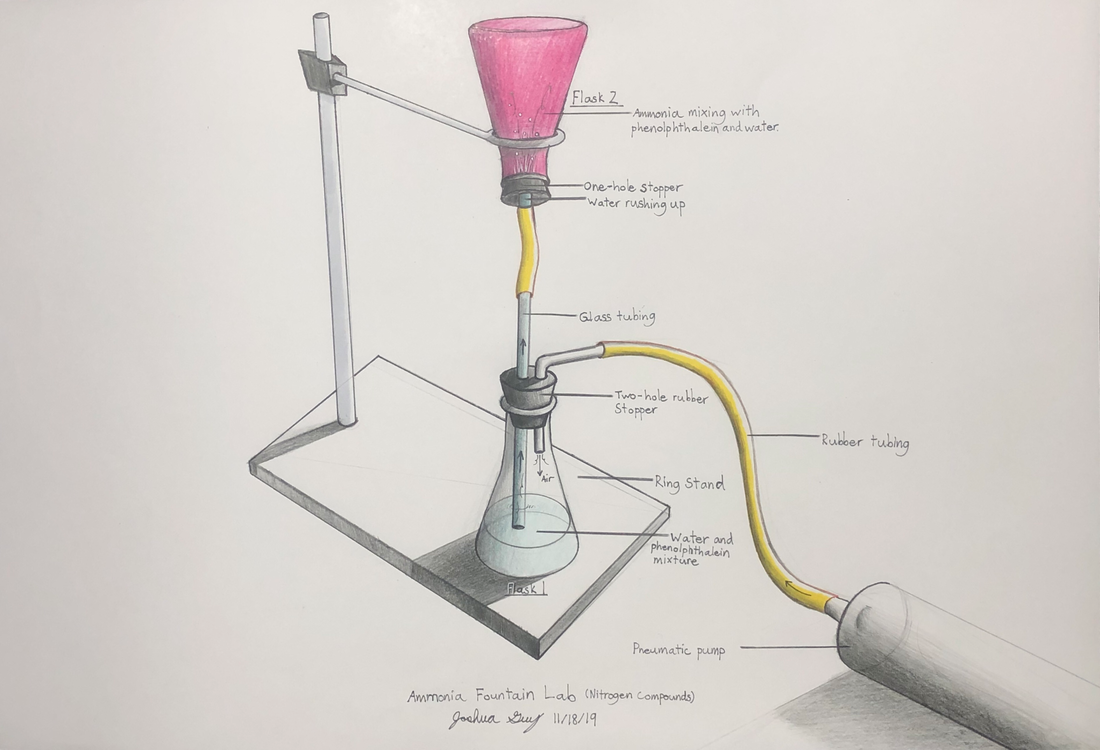
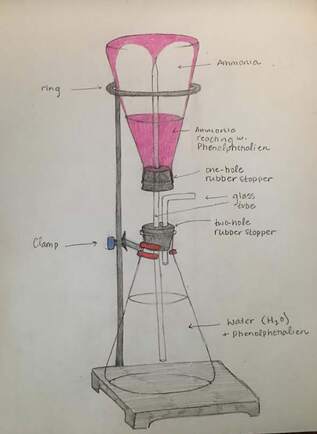
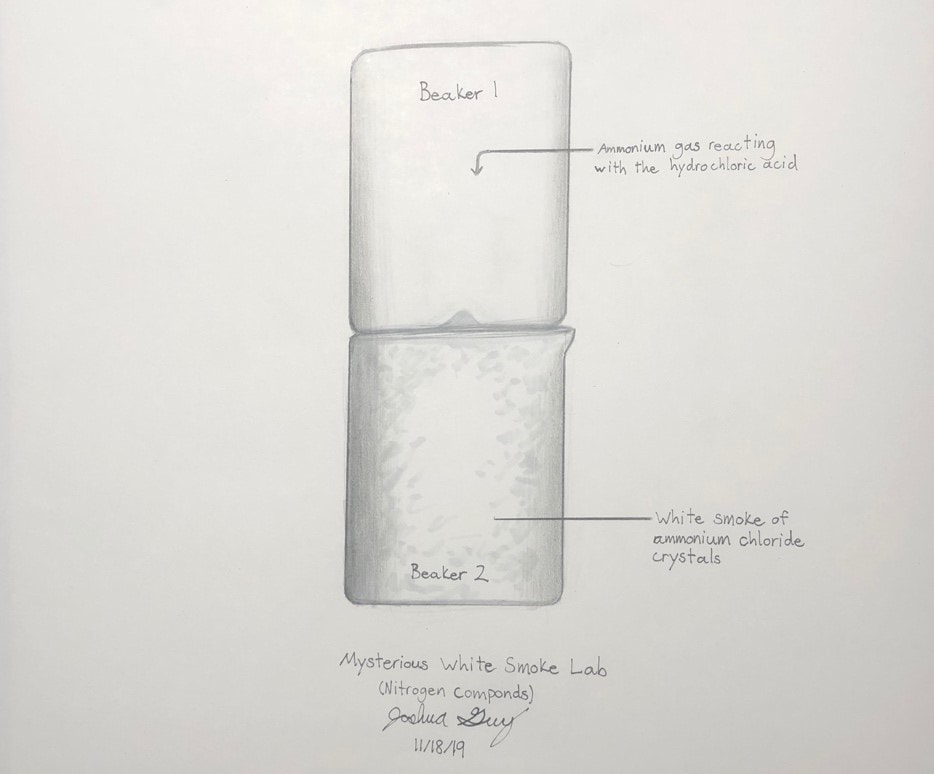
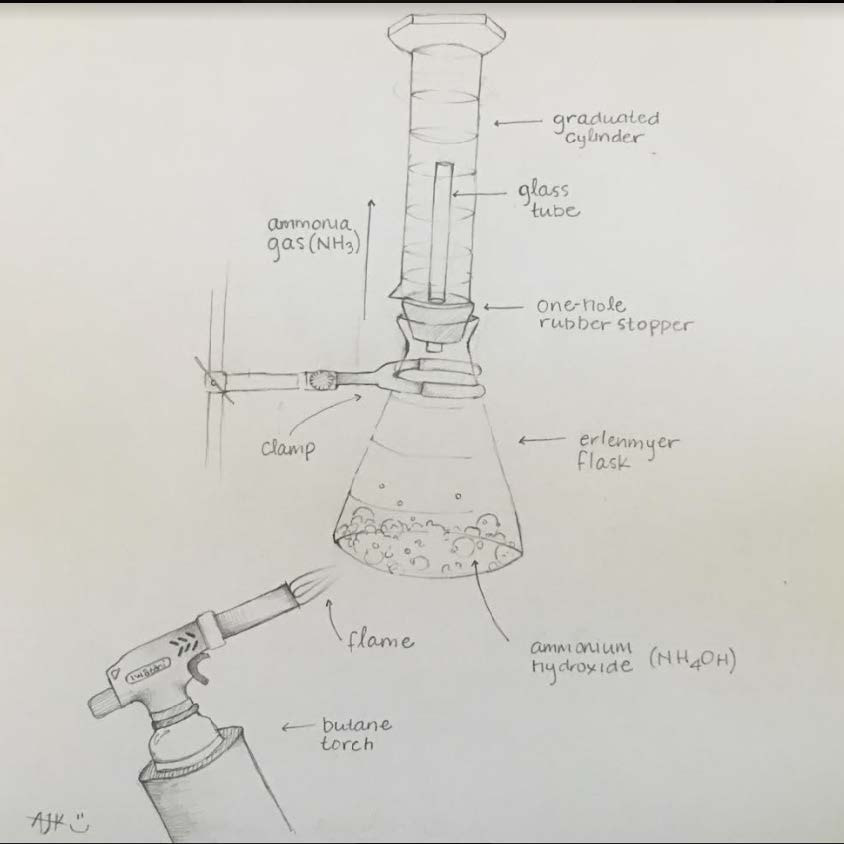
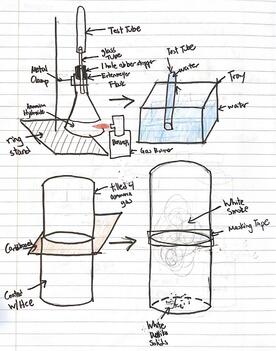
Nitrogen Compounds lab
We will make and test various nitrogen compounds.
We will make and test various nitrogen compounds.
- Nitrogen (N2) is the most prevalent element in "air", making up 78% of the earth's atmosphere.
- Nitrogen is the "lazy" element; it doesn't like to combine with anything else. You breath it in and out your whole life, and yet it does nothing in your lungs.
- You need nitrogen to make the amino acids necessary for you to live. All amino acids have nitrogen in them.
- Plants uptake nitrogen in the form of nitrates (NO3) and ammonium (NH4) found in the soil. Animals then eat the plants (and/or other animals) and get their nitrogen that way.
| nitrogen_compounds_lab_handout.pdf |
| nitrogen_cmpds_lab_-_student_examples.pdf |
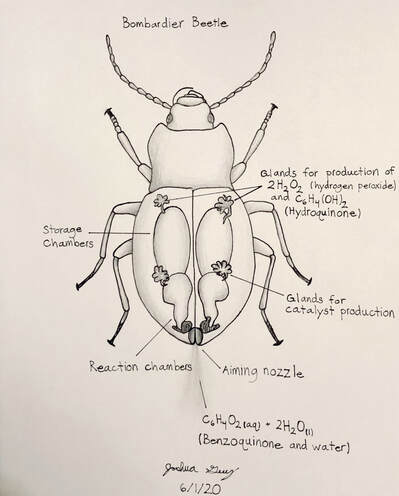
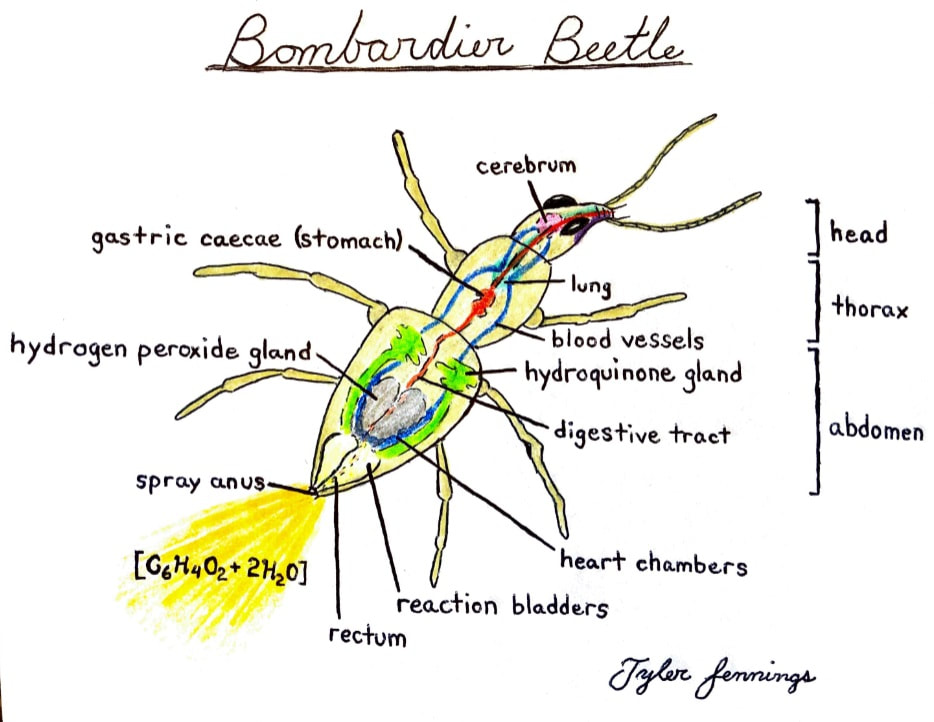
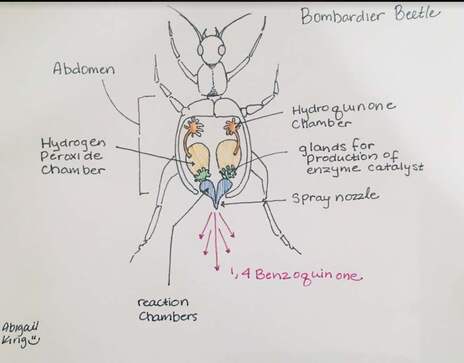
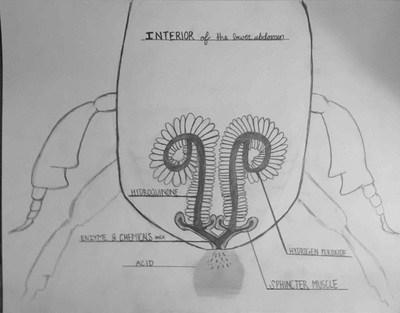
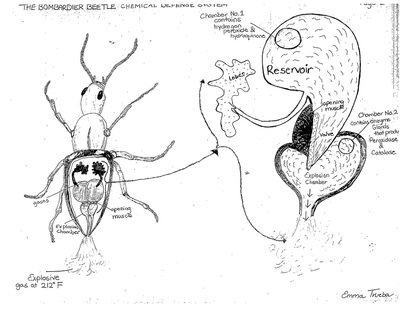
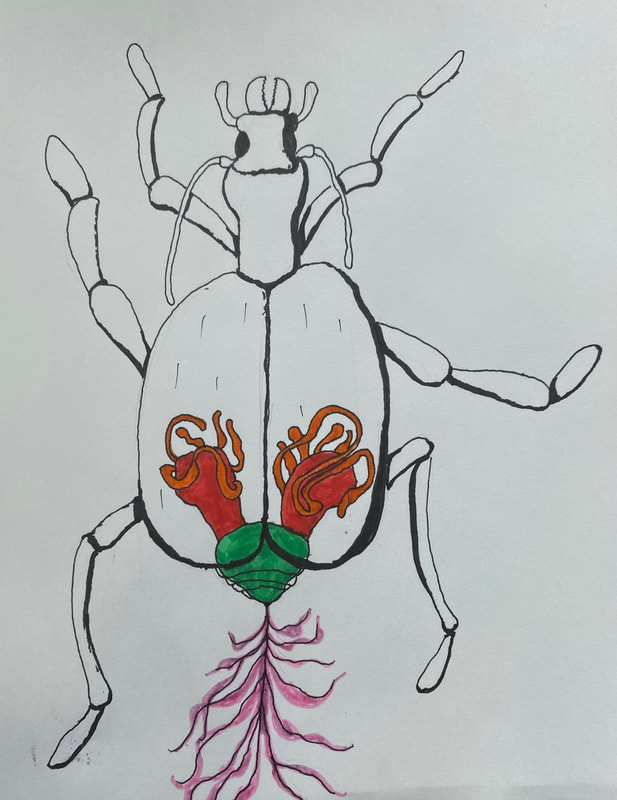
Bombardier Beetle research assignment
Research the following and submit a 1-1/2 to 2 page research paper: "The Bombardier Beetle uses an explosive discharge as a defensive measure. Explain and illustrate how this works and how this chases off the predator. Be sure to show the chemical reactions involved."
Research the following and submit a 1-1/2 to 2 page research paper: "The Bombardier Beetle uses an explosive discharge as a defensive measure. Explain and illustrate how this works and how this chases off the predator. Be sure to show the chemical reactions involved."
| Bombardier Beetle research papers - student examples |
Density lab
Turn in the 'student worksheet' part only
(Note to teacher: Simplify and combine these 2 documents before using)
Turn in the 'student worksheet' part only
(Note to teacher: Simplify and combine these 2 documents before using)
| density_lab_instructions.doc |
| density_lab_student_worksheet.doc |