Unit 1
Introduction to the human body
Reading
Ch. 1 Introduction
Lab
Stats in Physiology lab
Ch. 1 Introduction
Lab
Stats in Physiology lab
| Introduction lecture slides |
Summary
In this first Unit, we lay the groundwork for the study of Anatomy and Physiology
In this first Unit, we lay the groundwork for the study of Anatomy and Physiology
Video: Unlocking the Mystery of Life, 4 min.
Lecture outline
Note: The "lecture outline" each week is meant as a brief overview. You will still need to read the chapter!
Anatomy and Physiology deals with the structure & function of the human body
Levels of organization in the body
Note: The "lecture outline" each week is meant as a brief overview. You will still need to read the chapter!
Anatomy and Physiology deals with the structure & function of the human body
- Anatomy = structure (of each part)
- Physiology = function (of each part)
Levels of organization in the body
- Chemistry - atoms form the molecules of life
- Cells - molecules combine to form cells; the basic unit of all life
- Tissues - groups of similar cells form tissues; bone tissue, skin, muscle tissue, etc
- Organs - groups of tissues form organs; the heart, lungs, pancreas
- Organ systems - groups of organs form systems; for example the heart, lungs, and blood vessels form the cardiovascular system
The "Eleven Systems" of the human body. At this point, you just need to know what the terms mean. Throughout the course, we will cover each one in turn
Homeostasis
- Integumentary system (skin)
- Skeletal
- Muscular
- Nervous
- Endocrine (hormone producing glands)
- Cardiovascular
- Lymphatic (lymph vessels, nodes, spleen, immune system)
- Respiratory
- Digestive
- Urinary
- Reproductive (to be covered at home with parents)
Homeostasis
- This is a word you will encounter a lot, and means "equilibrium". The body maintains equilibrium through feedback systems, the nervous system, signaling molecules (hormones), and various receptor cells which monitor temperature, blood pressure, blood glucose, and many other things.
The "anatomical position"
Directional terms:
- This is where the human subject is depicted standing upright, facing the observer, with palms turned forward.
Directional terms:
- Superior = above
- Inferior = below
- Anterior = front
- Posterior = back
- Medial = nearer the midline
- Lateral = farther from the midline
- Proximal = nearer the body trunk
- Distal = farther from the body trunk
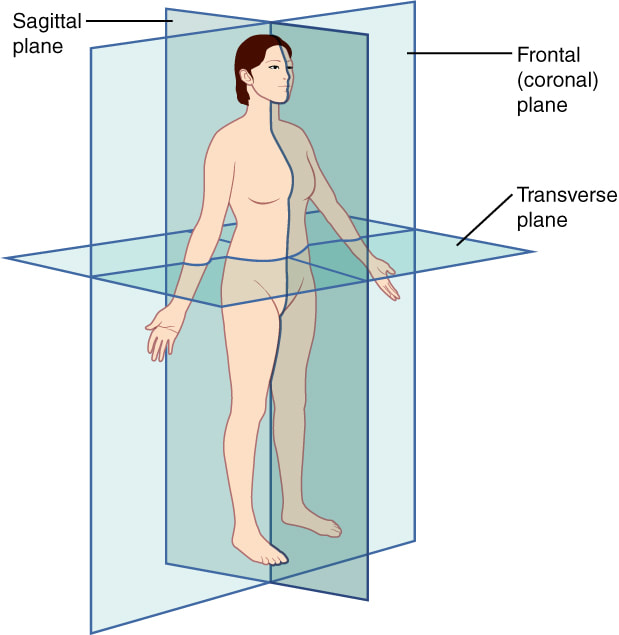
Body planes which the book uses
- Sagittal, Frontal, Transverse
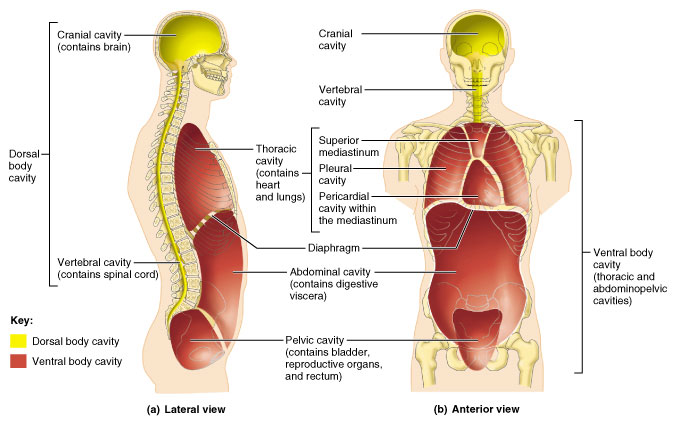
Body cavities:
- Cranial
- Vertebral
- Thoracic
- Abdominal
- Pelvic
- Also know where the diaphragm muscle is located
Statistics in Physiology lab
We will do the lab in class, and you will upload your completed lab report to Canvas by the due date.
If you would rather turn-in your completed lab report at class by the due date, that's fine too.
Required work: Part A "Assessments" questions #1-3, and Part B "Lab Extensions" questions #1-3 (#4-5 are not required).
We will do the lab in class, and you will upload your completed lab report to Canvas by the due date.
If you would rather turn-in your completed lab report at class by the due date, that's fine too.
Required work: Part A "Assessments" questions #1-3, and Part B "Lab Extensions" questions #1-3 (#4-5 are not required).
| 1._statistics_in_physiology_lab_handout.pdf |
Homework and handouts
| 1._introduction_to_human_body_homework_questions_2021.docx |
| Label_the_body_cavities_worksheet.pdf |
| planes_of_body handout.pdf |