Unit 3
The cellular level of organization
Reading
Read Ch. 3 "Cellular Level of Organization"
Read Ch. 3 "Cellular Level of Organization"
| Lecture slides: Cell Structure & Function |
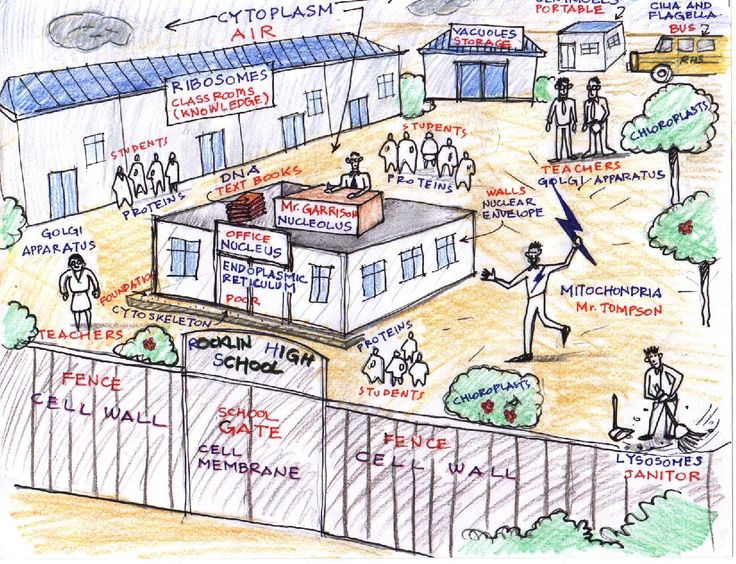
"Cell City": the inner workings of the cell can be portrayed as a modern factory, city or a school
Below: Our "Diagnosing Diabetes" lab will be an excellent launching pad for understanding the workings of the cell
Lecture topics
The plasma membrane (cell membrane)
The plasma membrane (cell membrane)
- Comprised of a lipid bilayer (two layers). The polar phosphate ends point outward, and the non-polar lipid tails point inward.
- The cell membrane is heavily imbedded with protein molecules, called 'membrane proteins'.
- Membrane proteins can be pumps of various types, signaling molecules, docking stations (receptors), enzymes, linkers, and cell identity markers.
- The membrane itself is permeable to nonpolar, uncharged molecules, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and a few other substances.
- Most other substances like glucose, amino acids, and protein molecules must be pumped or carried across the membrane.
- As mentioned above, substances can only pass across the cell membrane by simple diffusion, channel-mediated diffusion, or carrier-mediated diffusion. Your book covers these processes very well.
- Your book spends a lot of time on the sodium-potassium pump, for example. This transmembrane protein pump is important in nerve cells.
- Read the section on 'transport vesicles', which are like shipping containers within the cell.
- This is all the cell's contents located between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It includes the cytosol (the fluid portion) and the organelles (all the tiny structures or machines).
- We will discuss the organelles in class, and you should read this section of the chapter carefully and know what the organelles do.
- It is very helpful to use the 'Cell-city' or 'Cell-factory' analogy, here, when trying to remember what all these cell components do.
- The nucleus has its own protective membrane structure, called the nuclear envelope.
- The nucleus contains your chromosomes (23 from each parent, 46 total) which are made of DNA.
- DNA contains all your genetic information in a coded language of 4 characters.
- The details of DNA and genetics are covered in Biology.
Basic ideas
- Living things are built from cells; this applies equally to humans, fish, and corn plants
- This is pretty amazing when you think about it. Your body is comprised of trillions of little self-contained factories.
- Groups of similar cells are called "tissues". You have around 200 different types of tissues (bone, blood, muscle, etc)
- Groups of tissues are called "organs" (heart, pancreas, etc)
- Groups of organs are called "organ systems" (gastrointestinal 'GI' tract, cardiovascular system, endocrine system, etc)
Diagnosing Diabetes lab
Diabetes serves as an excellent launching pad for understanding cells & membranes, signaling molecules, and membrane transport mechanisms.
Diabetes serves as an excellent launching pad for understanding cells & membranes, signaling molecules, and membrane transport mechanisms.
| 3._diagnosing_diabetes_student_handout.pdf |
Human Cells homework questions
| 3._human_cells_homework_questions_2021.docx |
Cell Contents "Quiz"
| 3._cellular_contents_quiz_without_answers.pdf |
Diabetes research assignment
| 3._diabetes_research_assignment_instructions.docx |
| Diabetes sample student papers |
| More diabetes student papers |
"Cell Factory" homework assignment
Sketch a prototypical human cell and label the main components with their "actual" names and "factory/city" names. This is a really good way to learn the parts of the cell. Read the instructions below, and review the examples/ideas slides.
Sketch a prototypical human cell and label the main components with their "actual" names and "factory/city" names. This is a really good way to learn the parts of the cell. Read the instructions below, and review the examples/ideas slides.
| 3._cell_factory_assignment_instructions.docx |
| 3._cell_city-factory-restaurant_student_exemplars_anatomy_2017.pdf |
| 3._cell_factory_student_exemplar_k.m..pdf |
Cell Components in-class quiz
| cellular_contents_quiz_answer_key.pdf |
| cellular_contents_quiz_without_answers.pdf |
Other materials
| Lecture Slides: Diabetes |